Python resources for CS 237. Fast demo of Jupyter Notebooks. Markdown Tutorial: IPYNB. While it will be set to view only, please use the sheet to claim your resources, and comment in the threads with what you want and I will mark it down.

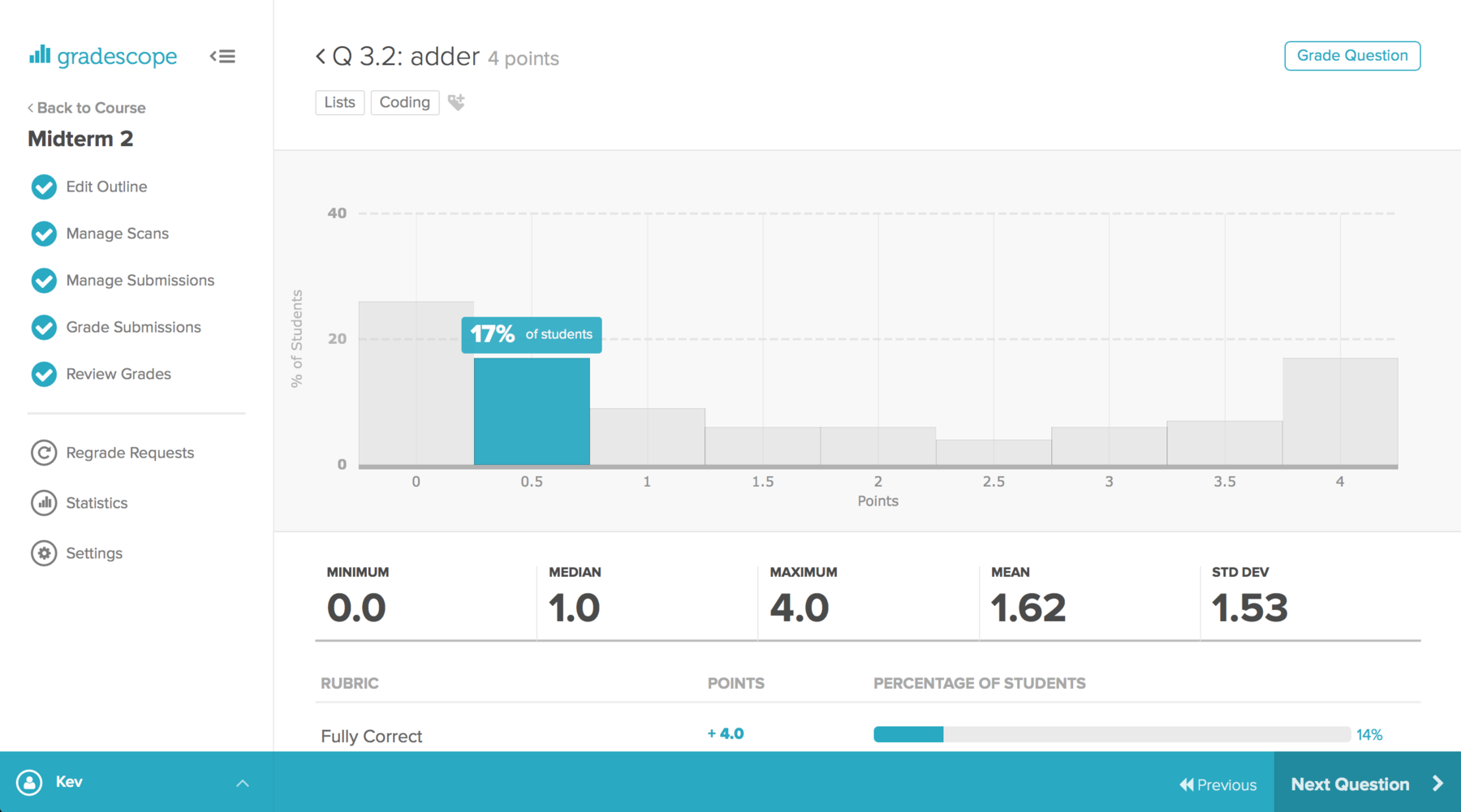

Gradescope Markdown Table
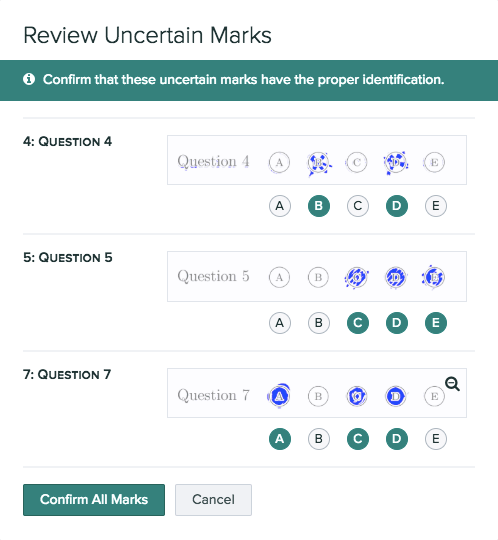
Gradescope Markdown Problems
Topics
Gradescope Market Cap

Gradescope Markdown Schedule
- Agile—A Software Development Methodology
- Agile: Standups—A timeboxed standing meeting to help team make progress
- Agile: Team Norms—Groundrules set by a team that promote effective and harmonious teamwork and productivty
- Agile: User Stories—As a (who?) I can (what?) so that (why?)
- Ant—Apache Ant, a build tool for Java (similar to Make/Makefiles)
- Antipatterns: —Things to avoid in your code
- Antipatterns: inheritance—When NOT to use inheritance
- APIs: —Application Programming Intefaces
- APIs: Free—Some APIs that offer free access
- Applications Programming—A compendium of knowledge and skills applications programmers (software developers) need
- Bug Reports—The typical format: STR, observed, desired
- Changelog—A Software Development Methodology
- CI: —Continuous Integration--automatically testing after every commit
- Code Review—A team activity to improve the code base and the product
- Code Smells—Common problems that arise in code
- Code Style—formatting, indenting, names, and much more
- Code Style: astyle—automatic code indenting tool available on CSIL
- Course Policies—Explanations of why certain instructors do things they way they do them.
- Course Policies: Answer Keys—Why do you not provide answer keys for all your old exams?
- CSIL—Computer Science Instructional Lab machines
- CSIL: browser from command line—How to open a browser from the command line
- CSIL: disk quota and file quota issues—How to diagnose and fix
- CSIL: git configuration—Configuring your CSIL account to use git
- CSIL: Remote Host Id Changed—The scary REMOTE HOST ID CHANGED message with mention of SOMETHING NASTY
- CSIL: ssh port forwarding—How to access webapps running on CSIL from your local machine
- CSIL: via ssh from Linux—Connecting via ssh from the command line
- CSIL: Via MacOS—Accessing CSIL from your MacOS system
- CSIL: via ssh from Windows—Connecting via PuTTY/XMing or MobaXterm
- Data—Various sources for datasets to build applications with
- Design: —Waterfall, Agile, Rational Unified Process, etc.
- Design Patterns—software structures that are easier to change
- Design Patterns: Strategy—Define multiple algorithms and let client application pass the algorithm to be used as a parameter.
- Eclipse—One of several choices for a Java IDE
- Enviroment Variables—Reading them from Java code
- Firebase—A Google sponsored app development platform
- Frameworks—Software that helps you write other software
- Game Programming—How to make Java work for Games
- Gauchospace: Clickable URLs—In assignment submissions, urls should be clickable
- git and github—version control, source code configuration and project collaboration tools
- git: basic workflow—The basics: git add..., git commit..., git push ...
- git: cloning your first repo—A guide for those new to git
- git: commit messages—How to write clear and helpful commit messages
- git: feature branch workflow—One branch per feature/issue/story
- git: git/github troubleshooting—Various problems and their solution
- git: .gitignore files—What they are for and what to put in them
- git: merge conflicts—Not nearly as scary as you may have been told
- git: overview—An introduction. git vs. github.com vs. github.ucsb.edu, repos, etc.
- git: throwaway untracked files—how to clean up untracked files easily
- github: adding collaborators—giving individual users access to a private repo
- github: api—Java Api for Github
- github: branch protection—making sure PRs to master get code reviewed, for example
- github.com: creating private repos under an organization—for closed source class assignments
- github: issues—working with issues in github
- github: keyboard shortcuts—making the github web UI easier to use
- github: pro tips—A few extras to help you work with GitHub more effectively
- github: using ssh keys—generating public/private key pair, uploading public key to github
- github: ucsb-cs-github-linker—Using the local tool to join a course organization
- github.ucsb.edu: creating private repos under an organization—for closed source class assignments
- github: verified badge on commits—adding extra security to your commit messages
- Google:—Using Google Products in CS48
- Google: Cloud Credits—What they are good for, and how you can get them
- Google: Developer Console—The place you configure OAuth, APIs, etc.
- Gradescope—System for homework grading, feedback and submission
- Gradescope: Organization Access—How to enable access to organization repos
- Gradescope: Regrade Requests—What to do if you have questions about the grading of a problem (e.g. you think there was a grading error)
- Gradescope: Student Self-Submission—Scanning your assignment to PDF
- Heroku—A cloud computing platform
- Heroku: Troubleshooting—Solutions to common problems and errors
- IDEs for Java—Integrated Development Environments for Java (IntelliJ, Eclipse, Netbeans, etc.)
- JDBC—Java Database Connectivity--a way to use SQL-based databases with Java
- Jekyll—Creating web sites (like this one) on github-pages using Markdown
- JSON: —JavaScript Object Notation
- JSON: Jackson—A Java Package for processing JSON
- Kanban: —visualization of work in progress
- localhost—What does it mean to run a web server on localhost?
- Lombok: —Automatic generation of getters/setters, etc.
- MacOS—Setting up an environment to do CS56 work on your own Mac (not ssh'ing into CSIL)
- MacOS: Homebrew—Package installer for Mac OS
- Markdown—A simplified syntax to create formatted documents
- Maven—A build tool for Java plus a package manager
- Minimum Viable Product (MVP)—Simplest thing that a customer would actually use
- MongoDB—A particular NoSQL database platform
- MongoDB: Cloud Atlas Setup—Setting up MongoDB Cloud Atlas (for new users)
- MongoDB: Cloud Atlas Sharing—Sharing a Cloud Atlas Setup
- MongoDB: Mlab—A cloud provider of MongoDB databases with a free tier
- MongoDB: NextJS Guide—How database operations in NextJS differ from examples in standard node
- MongoDB: NextJS Setup—Configurig your NextJS app for MongoDB
- MongoDB: Spring Properties—How to set properties for connecting to MongoDB when using Spring
- Node—A JavaScript based backend web framework
- OAuth—The way we implement the 'login with Google, Facebook, or Github' thing you see on some websites
- OAuth: Authorizing GitHub Third Party Apps—Gradescope, and GitHub OAuth Apps you build yourself
- OAuth: GitHub Setup—Setting up a GitHub OAuth App to obtain client id and client secret
- OAuth: Google Setup—Setting up a Google OAuth App to obtain client id and client secret
- OOP—Object Oriented Programming
- Personas—Ficticious users of our product that help us develop our stories
- PL: —Programming Languages (comparisons, analysis)
- Port Numbers—Those numbers such as 8080, 12345 that show up when doing networking things
- Postgres—An implementation of an SQL relational database, available on Heroku
- Postman—A tool for testing HTTP based APIs
- Python: OpenCV—Installing OpenCV for Python
- React—A front-end framework for webapps and native apps
- Refactoring—
- REST—RESTful APIs, etc (Representational State Transfer)
- Retros: —The heart of agile is inspect and adapt; retrospective meetings ('retros') help make sure we do that
- Retros: Darby/Larsen Five Step Retro—(1) Set Stage, (2) Gather Data, (3) Generate Insights, (4) Decide What To Do, (5) Close Retro
- Retros: Stop-Start-Continue—A three step formula for running a retro
- Scrum—A Software Development Methodology
- Selenium—Remote Control of a Browser (e.g. for end-to-end testing of webapps, web scraping)
- Selenium: Driver Setup—Setting up your driver
- Semantic Versioning—A set of rules for assigning meaningful version numbers
- Slack—A chat-based communication tool for teams
- Sockets—An abstraction used in networking
- Software Engineering—What is meant by this term?
- Spring Boot: —A Java web application framework
- SQL—SQL-based relational databases (sqlite3, Postgres, MySQL, etc.)
- Style—Standards and Tools for Code Style
- $T and $B—Using environment variables to make navigating a src tree less painful
- TDD: (Test Driven Development)—General information about best practices
- Teams: —Information about working in teams
- Teamwork—Practices for setting up a harmonious and productive team
- Test Driven Development (TDD)—General information about best practices
- Testing—Everything having to do with testing: Unit testing, Integration Testing, Test Coverage
- Testing: Acceptance Testing—Criteria for being 'done' with an issue
- Testing: Agile Testing (Crispin and Gregory)—Material from the book by Lisa Crispin and Janet Gregory, Agile Testing: A Practical Guide for Testers and Agile Teams
- Testing: Automation—How to make testing an automatic part of your process
- Testing: End to End Testing—Intro to End to End Testing, and Framework Specific Examples
- Testing: Jacoco Reports—How to interpret the reports (red, yellow, green)
- Testing: Jacoco via Maven—Setting up Jacoco test coverage, using Maven
- Testing: Unit Testing with Jest—Setting up Jest for Next.JS projects
- Testing: Mocking—Intro to Mocking in Tests, and Framework-specific Examples
- UML—Unified Modeling Language: A graphical language for software design
- Unix (and Linux)—A variety of resources related to Unix and Linux, esp. command line tools
- Unix: Misc tools—Various useful command line tools you may not know about
- Unix: Search/Replace across multiple files—from the command line, using grep, sed, etc.
- User Stories: —As a (who?) I can (what?) so that (why?)
- User Stories: INVEST—Good user stories are: Indepenent, Negotiable, Valuable, Estimatable, Small and Testable
- vim—a widely used text editor among Unix users
- vim: basic eight—eight things you need to know how to do for your survival
- vim: customization—customizing vim for your purposes
- vscode—Visual Studio Code, a lightweight free editor from Microsoft with many IDE features
- Waterfall—A model of the Software Design Life Cycle (SDLC) from the 1970s
- Windows—Setting up an environment to do CS56 work on your own Windows machine (not ssh'ing into CSIL)
- Windows: WSL—Setting up the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
- X11—Dealing with X11 DISPLAY issues
- YAML—An alternative to XML and JSON for representing structured data in a machine and human readable format
- Zoom—Teleconferencing tool
