Tutorial
- Apache Http Server Reverse Proxy Download
- Apache Reverse Proxy Windows
- Apache As Proxy Server
- Apache Http Server Reverse Proxy Download
- Apache Http Server Reverse Proxy Windows
Introduction
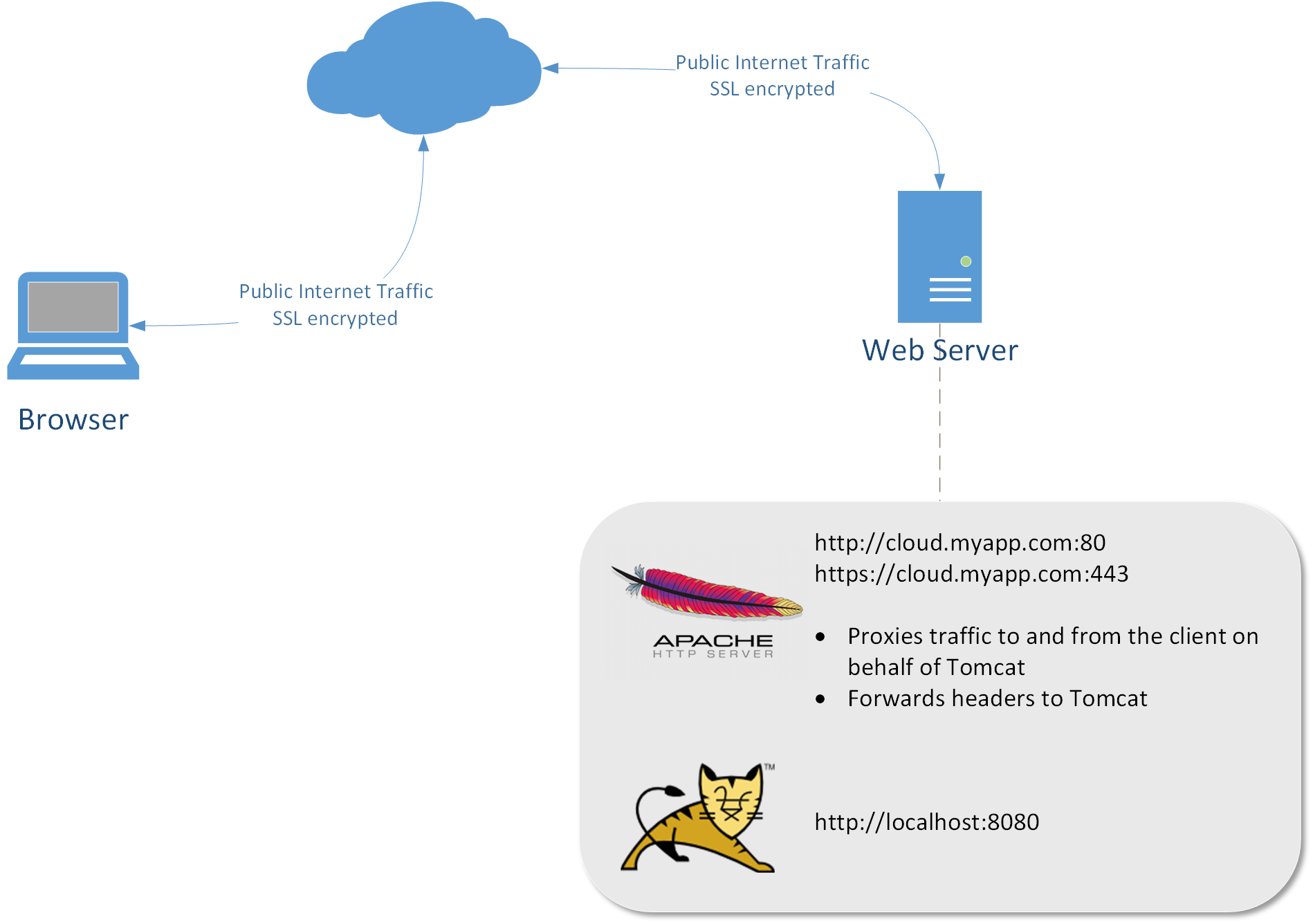
This is essential when Apache is used as a reverse proxy to avoid by-passing the reverse proxy because of HTTP redirects on the backend servers which stay behind the reverse proxy. Path is the name of a local virtual path. Url is a partial URL for the remote server - the same way they are used for the ProxyPass directive. Instructions (Run All on the Reverse Proxy server – for this example it is 10.1.1.2) Set up Apache On the reverse proxy server, install apache web server and enabled the required modules by executing the lines below in terminal. Reverse proxy caching (also known as server acceleration) is different because Traffic Server acts as a proxy cache on behalf of the origin servers that store the content. Traffic Server is configured to behave outwardly as origin server which the client is trying to connect to. After our research, we found that Apache Web Server configurations need to be done to get it working. In general, it is called WebSocket reverse proxying (“Reverse Proxy” settings with “wstunnel”).
Apache Http Server Reverse Proxy Download
Apache is a tried and tested HTTP server which comes with access to a very wide range of powerful extensions. Although it might not seem like the go-to choice in terms of running a reverse-proxy, system administrators who already depend on Apache for the available rich feature-set can also use it as a gateway to their application servers. In most cases, this will translate to removing an additional layer from their server set up or the need to use yet another tool just to redirect connections.
In this DigitalOcean article, we are going to see set up Apache on Ubuntu 13 and use it as a reverse-proxy to welcome incoming connections and redirect them to application server(s) running on the same network. For this purpose, we are going to use and work with the mod_proxy extension and several other related Apache modules.
Glossary
1. Apache
2. Apache Working As A Reverse-Proxy Using mod_proxy
3. Installing Apache And mod_proxy

- Updating The Operating-System
- Getting The Essential Build Tools
- Getting The Modules And Dependencies
4. Configuring Apache To Proxy Connections
- Activating The Modules
- Modifying The Default Configuration
- Enabling Load-Balancing
- Enabling SSL Support
- Restarting Apache
Apache Reverse Proxy Windows
Apache
Apache HTTP server does not require an introduction, since it is probably the most famous and popular web-server that exists. It is possible to run Apache very easily on many different platforms and set ups. The application comes with a lot of third party modules to handle different kind of tasks (mod_rewrite for rule-based URL rewriting) and one of them, albeit nowadays relatively neglected, is mod_proxy: The Apache Module to implement a proxy (or gateway) for servers running on the back-end.
Tip: According to some articles, Apache’s name comes from server’s “patchy” nature - i.e. it being a collection of application patches (or modules).
Note: To learn more about Apache, you can check out the Wikipedia entry on the subject - Apache HTTP Server.
Apache Working As A Reverse-Proxy Using mod_proxy
mod_proxy is the Apache module for redirecting connections (i.e. a gateway, passing them through). It is enabled for use just like any other module and configuration is pretty basic (or standard), in line with others. mod_proxy is not just a single module but a collection of them, with each bringing a new set of functionality.
Some of these modules are:
mod_proxy: The main proxy module for Apache that manages connections and redirects them.
mod_proxy_http: This module implements the proxy features for HTTP and HTTPS protocols.
mod_proxy_ftp: This module does the same but for FTP protocol.
mod_proxy_connect: This one is used for SSL tunnelling.
mod_proxy_ajp: Used for working with the AJP protocol.
mod_proxy_wstunnel: Used for working with web-sockets (i.e. WS and WSS).
mod_proxy_balancer: Used for clustering and load-balancing.
mod_cache: Used for caching.
mod_headers: Used for managing HTTP headers.
mod_deflate: Used for compression.
Note: To learn more about Apache and mod_proxy, you can check out the official Apache documentation on the subject here.
Installing Apache And mod_proxy
Note: Instructions given here are kept brief, since chances are you already have Apache installed or know how to use it. Nonetheless, by following the steps below you can get a new Ubuntu VPS running Apache in a matter of minutes.
Updating The Operating-System
We will begin with preparing our virtual server. We are going to first upgrade the default available components to make sure that we have everything up-to-date.
Update the software sources list and upgrade the dated applications:
Getting The Essential Build Tools
Let’s continue with getting the essential package for application building - the build-essential. This package contains tools necessary to install certain things from source.
Run the following command to install build-essential package:
Getting The Modules And Dependencies
Next, we are going to get the module and dependencies.
Run the following command to install them:
Configuring Apache To Proxy Connections
Activating The Modules
Before configuring Apache, we are going to enable the necessary modules that we will be using in this tutorial, or which might come in handy in the future.
First, let’s verify that all modules are correctly installed and ready to be activated.
Run the following command to get a list of available Apache modules:
Once you are prompted with the choice of modules you desire, you can pass the below line listing the module names:
The list of modules:
Or alternatively, you can run the following commands to enable the modules one by one:
Note: Some modules are likely to be enabled by default. Trying to enable them twice will just ensure that they are active.
Modifying The Default Configuration
In this step, we are going to see how to modify the default configuration file 000-default.conf inside /etc/apache2/sites-enabled to set up “proxying” functionality.
Run the following command to edit the default Apache virtual host using the nano text editor:
Here, we will be defining a proxy virtual host using mod_virtualhost and mod_proxy together.
Copy-and-paste the below block of configuration, amending it to suit your needs:
Press CTRL+X and confirm with Y to save and exit.
Note: To learn more about virtual host configurations, you can check out the detailed Apache manual on the subject by clicking here.
Enabling Load-Balancing
If you have multiple back-end servers, a good way to distribute the connection when proxying them is to use Apache’s load balancing features.
Start editing the virtual-host settings like the previous step, but this time using the below configuration example:
Enabling SSL Reverse-Proxy Support
If you are dealing with SSL connections and certificates, you will also need to enable a secondary virtual host with below settings.
Repeat the steps from the previous steps but using these configuration options:
Restarting Apache
Apache As Proxy Server
Once you are happy with your configuration, you will need to restart the cloud server for the changes to go into effect.
Execute the following command to restart Apache:

And that’s it!
You can now visit your VPS and Apache shall reverse-proxy connections to your back-end application servers.
This brief tutorial shows students and new users how to install and configure reverse proxies with Apache2 HTTP Server on Ubuntu 18.04 and others..
Reverse proxy is when a proxy server (in this case, Apache2 HTTP) accepts all traffic and forwards it to a specific resource, like a backend server or container.. The backend server can be either another Apache2 or open source HTTP server like Nginx…
Apache2 HTTP server is one of the most popular open source web servers that is in use today… It’s not typically used as a proxy server, but can be if you want to use it as one..
There are many reasons to install and use a proxy server… Example, reverse proxy can be used to added security, or for load balancing, restrict access to certain locations in order to prevent attacks and many more…
When you’re ready to configure Apache2 as reverse proxy, follow the steps below:
Step 1: Install Apache2
Installing Apache2 is easy.. to do that, simply run the commands below
After installing Apache2, the commands below can be used to stop, start and enable Apache2 to always restart when the server boots up.
To test Apache2 setup, open your browser and browse to the server hostname or IP address and you should see Apache2 default test page as shown below.. When you see that, then Apache2 is working as expected..
Step 2: Configure Apache2 as Reverse Proxy
Assuming that Apache2 is installed and ready, you can now configure Apache2 to act as a reverse proxy..
Apache2 proxy module’s ProxyPass and ProxyPassReverse function provide a reverse proxy… To use ProxyPass and ProxyPassReverse, you must first know where you want to direct traffic..
In a typical setup, the reverse proxy server will listen for all traffic on the default HTTP port, which is port 80..
The backend server which host the content will listen on a custom port… Most likely port 8080.
In this post, we’re going set up Apache2 to listen on port 80, then direct traffic to the backend server which listens on port 8080
Below, run the command to create a proxy VirtualHost file called Apache2Proxy.conf.
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/Apache2Proxy.conf
Then add the block of codes in the file then save.
Save the file when done.
The file contains your server name as well as the proxy_pass where traffic are directed when received by the proxy server….
Step 3: Enable Apache2 Proxy
Now that Apache2 is installed, run the commands below to enable its proxy modules.
When you’re done, enable the VirtualHost site and restart Apache2 to enable reload the modules.
Launch a web browser and navigate to your server hostname (example.com)… You will now be proxied to your Apache2 server on port 8080.
Apache Http Server Reverse Proxy Download
Congratulations! You have successfully configure Apache2 reverse proxy on Ubuntu 18.04
Apache Http Server Reverse Proxy Windows
You may also like the post below:
